A poem analysis essay resembles a poetry review:
You read a poem, examine it, and interpret it for readers to understand its meaning, structure, and purpose, as well as the literary devices the author used to communicate the message.
In this blog post, you’ll learn how to write a poem analysis essay. Get ready to find insights and practical tips from our writers, together with an outline template and examples to consider when writing your poem analysis.
We’ll walk you through the whole process:
Table of contents
Poem Analysis Essay: Definition and Specifics
A poem analysis essay is a type of academic paper students write in school or college to review a poem. It includes reviewing, examining, and interpreting the poem’s structure, meanings, themes, and symbols, as well as the literary devices the poet used.
In plain English, you do a poetry analysis to explain all the creative writing ideas a poet uses to communicate the desired message to readers.

Why explain poems to readers?
Poetic language differs from natural human speech and other forms of written language. Full of hidden symbols, imagery, and meanings, it’s often hard for an average reader to understand. While they may have some guesses on what the poet was attempting to convey, most poems have multiple meanings that we can only see through close, in-depth reading and analysis.
Poetry is concise yet descriptive, where a single word can convey multiple ideas. Those meanings may be elusive, and here’s where poetry analysis comes into play:
It helps us read between the lines and understand the poet’s feelings and intentions behind their words.
Why write poem analysis essays in college?
Educators assign poem analysis essays for the following reasons:
- To help you develop critical thinking and analytical skills
- To help you learn to make a text-based argument and defend ideas based on the text
- To teach you to understand what you’re reading
- To assess your knowledge and understanding of the subject, especially if you’re in a literature class or studying the arts
- To encourage you to enjoy poetry and nourish your creative thinking with it
Poem Analysis Format: Elements to Include
A poem analysis essay involves a detailed examination of various literary elements. Besides general information about a poem (its title, author, publication date, and background), you should cover many elements: structure, theme, rhythm (tone and intonation), rhyme scheme, figurative language (imagery and symbols), poetic devices, and mood.
A poem analysis format may also include the target audience:
- To whom did the author write the work?
- What was the context?
Thus, we can understand a poem about peace differently if we know that it was written during World War II and addressed Germans.
So, let’s dig deeper and get more information on every element to include in your poem analysis essay. Here go all seven:
- General information about the poem
- Poem structure
- Music of the poem
- Tone and intonation
- Central theme
- Imagery and symbols in the poem
- Poetic devices

General information about the poem:
Start your essay by introducing the poem to readers. Share information about the title, author’s name, publication date, and context of the poem to grab the reader’s attention and get them interested in learning more.
Speaking of the title, by the way:
Do your best to analyze it to gain insights into the poet’s intentions and the poem’s overall atmosphere. First, examine its literal meaning: Look for keywords and phrases that stand out and consider their connotations and the associations they evoke. Then, look for symbolism in the title: Does it have a deeper meaning beyond its literal interpretation?
(Explore multiple interpretations and reflect on how they can influence your overall understanding of the poem.)
Also, think about why the poet decided to name their work like this. Does the title summarize the poem’s ideas? Does it add complexity to its themes?
Once you read the poem, compare the title with the final lines. When analyzing the relationship between the title and the poem’s conclusion, it can take on a new meaning.
Poem structure:
Determine the poem’s form: Is it a verse, a haiku, a sonnet, a ballad, or something else? Examine how the poem’s parts relate to each other and what each part discusses:
- What logical sense does it have?
- Can we evaluate any emotional sense in the poem?
Analyze the poem’s structure: If it’s a strict format, does it tell us anything about the poet? If the poem’s narrative structure is torn or vague, is there any meaning or message behind that being the case?
A detailed examination of the poem’s music will help you understand the structure better.
Music of the poem:
When we speak about the poem’s music, it’s about the following elements each lyrical work has:
- Stanza, aka a verse (How do the poem’s lines join together or separate from each other?)
- Meter (What is the composition of stressed and unstressed syllables in the poem? The most common meter in English literature is iambic pentameter, which has five beats per line.)
- Rhyme (What is the poem’s specific rhyme scheme, if any? Is it AABB, ABAB, or ABBA? The lack of a regular rhyming pattern can also signal a particular mood for the poem.)
- Rhythm (The poem’s meter determines its rhythm, creating a particular beat that communicates the poem’s mood. For example, a fast beat can make the poem sound happy.)
- Sound effects (Does the author use isocolon, litotes, repetition, specific punctuation, or other techniques to emphasize certain phrases, convey a particular tone, and contribute to the poem’s overall meaning?)
Tone and intonation:
The tone and intonation of the poem help you understand the poet’s mood and attitude towards the theme they are discussing.
Consider the word choice: Look for words with strong connotations that evoke emotions (joy, anger, sadness, etc.) and create a specific mood. Analyze how the poet structures sentences and what syntax they use to influence the tone.
For example, short, abrupt sentences communicate tension or urgency, while longer, flowing ones convey contemplation or relaxation. Word choice and sentence syntax are great weapons for persuading the audience and influencing their emotions.
| Extra read: Check our detailed guide on how to write a persuasive speech and use particular words and emotional writing tactics to influence readers. |
Central theme:
Analyze the poem’s purpose. What were the poet’s intentions and motivations for creating this work? What message did they want to convey?
Identify the main themes and ideas: Is it love, social justice, nature, morality, or something else? Reflect on the poet’s background and analyze how it may have affected their choice of subject matter. Analyze how the poetic devices they use contribute to the poem’s purpose.
Imagery and symbolism in the poem:
Analyze the poetry’s language. What language, descriptions, and literary devices does the poet use to create images in the reader’s mind and present the meanings? Pay attention to visual, auditory, and tactile images; try to figure out the symbols used in the poem, their significance, and their potential interpretations.
Poetic devices:
These are literary techniques (i.e., examples of figurative language) poets use to enhance their work’s meaning, tone, and intonation. Pay attention to metaphors, similes, personification, irony, metonymy, and other devices. Analyze how they contribute to the meaning and perception of the poem.
Now that you know how to analyze a poem in an essay, let’s see how to format your paper and structure it for better readability and clarity.
Poetry Analysis Essay Outline Template
Once you’ve read the poem several times and analyzed its elements, combining everything in a concise poem outline, plan out the structure of your essay.
Like any other academic paper, a poem analysis essay has a standard structure of three core parts:
- An introduction
- A body representing all the above-discussed elements
- A conclusion
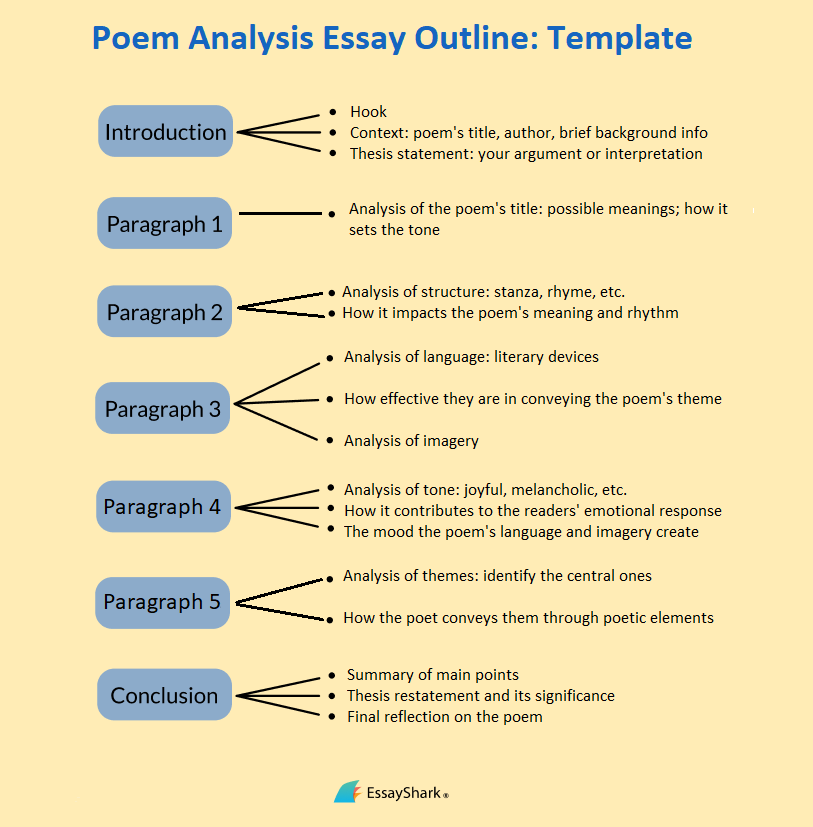
Here’s how to introduce a poem in an essay:
The opening sentence of your essay sets the tone and provides the context. Include the following:
- The title, author’s name, and publication date of the poem you’ll analyze
- Some brief background information about the poem and its context
- Your thesis (the central argument or poem interpretation)
Remember to use a hook to grab the reader’s attention from the start: Ask a question or share an intriguing statement in the first sentence to encourage the audience to keep reading.
What do you write in the body of your poem analysis essay?
Divide the body of your essay into 4-5 paragraphs:
- Poem title analysis
- Structure analysis
- Language and imagery analysis
- Tone and mood analysis
- Themes and meaning analysis
When analyzing, remember to back up your points with evidence. Use quotes from the poem to support your statements about its structure, tone, themes, and purpose.
How to conclude your essay:
The final paragraph of your poem analysis essay summarizes your main points, restates the thesis, and provides a final reflection on the poem and its impact.
How to Write a Poem Analysis Essay Step-by-Step
All the above may sound confusing and too challenging to handle, but it’s not. Practice makes perfect, and the more essays you write, the easier and faster the process becomes. The secret is to remember all the steps on how to write a poetry essay and turn them into your writing routine, thereby automating it.
| Reminder: If you have doubts or questions about your college assignments, whatever the type, you can ask our writers and get professional help fast. For those craving extra tips on writing a poetry analysis essay, keep reading! |
Below is your quick guide on how to write a poem analysis essay:
?hoose a Poem for Analysis
If your teacher or prompt doesn’t prescribe any particular poem for you to analyze, ensure that you choose an appropriate one yourself. Instruments like a title generator for essay and an essay prompt generator free will ease the process, but consider the following aspects:
- Look for poems that are relevant to the themes you need to cover.
- Consider those that also resonate with you emotionally.
- Choose poems with complex and deep meanings so that you have a field for analysis. (Poems that are too straightforward won’t provide enough materials to explore and interpret.)
Read It Aloud
Poems relate to both oral and written art, so they often apply sound techniques you’ll detect more easily when reading aloud. (You’ll need them when analyzing the poem’s tone and music, remember?)
Read the work you’ll discuss in your poem analysis essay several times:
First, read it without an analytical focus but with reflections on how you respond to the poem. How did it make you feel? What do you think the author was trying to say?
Then, read it aloud once again to specify technical details like the stanza, meter, and rhyme. How do they contribute to the poetry’s tone and mood? Note it down; you’ll need this information later to analyze the rhythm and intonation.
Finally, read it again to finalize your impressions and interpretations of the poem’s purpose and meaning.
Identify Its Type and Double-Check the Meanings
All poems fall into three categories:
- Free verse
- Formal verse
- Prose poems
Which is yours?
Depending on the type, you will ask yourself certain analytical questions while analyzing it. For example, if it’s a prose poem, you’ll need to determine what exactly makes it a poem rather than a short piece of prose. If it is a formal verse, specify what form this verse has: sonnet, villanelle, haiku, sestina, vial poetry, etc.
When wondering how to write an essay about a poem, you’ll focus on the poem’s type and structure to collect all the other details necessary for the in-depth analysis.
Collect All the Details You Need to Format It

Examine and analyze the poem’s narrative, contents, main ideas, and hidden meanings — the above-discussed elements you’ll need to include in the body of your poem analysis essay.
Outline Your Essay
You already know about what a poetry analysis essay outline is. Once you’ve analyzed the poem and noted down all the elements and interpretations, craft the plan:
Write down what you’ll mention in the essay’s introduction, how you’ll structure the body paragraphs, and what you’ll write in the conclusion. The outline allows you to write a compelling and coherent paper with no risk of missing critical details or messing up the logical flow.
Write the Draft
Write your paper, following the outline paragraph by paragraph. Here are some stylistic tips on how to write a poem analysis essay:
- Use present tense.
- Use quotations from the poem when explaining their meanings and relations to your arguments. (You can also support your points by citing other reputable critics whose points are relevant to your argument.)
- Use the MLA citation format unless otherwise stated in your assignment guidelines.
Proofread and Edit Your Poem Analysis Essay
Once your draft is ready, take your time to revise and polish it:
Ensure that you’ve mentioned all the elements supporting your argument or interpretation. Check if your essay follows the guidelines and is free from spelling, grammatical, and punctuation mistakes.
You can also scan it via a plagiarism checker to prevent accidental duplications and accusations of violating academic integrity. (A paraphrasing tool online free can help you rewrite the problematic passages for better originality.)
Given that many teachers and educational institutions also check if students use AI tools to craft their papers, scan yours via an AI detector to see if it has AI text patterns. Then, polish accordingly.
Need an Example?
With so many poem analysis essay examples available online today, it’s easy to get lost and confused about which ones are relevant and worth your attention. For a better understanding of how to write a poem analysis essay, feel free to use this sample from our academic writers:

How to Write a Poem Analysis Essay: Key Points
Consider this your quick checklist on how to write a poem analysis essay to follow when dealing with such an assignment from teachers or editors.
| Choose a relevant poem for analysis: something thematic, resonating, and complex enough to explore and interpret.Read it multiple times to get initial impressions and grasp the meanings.Analyze the title: How does it reflect the poem’s themes, contents, and purpose?Examine the poetry’s structure: stanza, meter, rhyme, and rhythm.Analyze the figurative language (imagery and symbols) the poet used to communicate the meanings and make their work sound better.Examine the tone and intonation of the poem: What mood does it create? How does it contribute to its overall message and purpose?Consider the poet’s intended audience when reflecting on the purpose of their work.State a clear thesis in the introduction of your analysis essay, presenting your interpretation of the poem.Write body paragraphs, each focusing on a specific element (structure, language, tone, theme, etc.).Support your points with evidence from the poem. (Use quotations as examples.)Conclude your paper by summarizing your points and explaining the significance of your findings. Reflect on the poem’s impact and leave the reader with food for thought. |
To Be, or Not to Be, That Is the Question
A poem analysis essay is about examining and interpreting a literary work. The poem’s structure, language, and imagery are all elements that help us understand the meanings and interpret the poet’s work the way they intended it.
Reveal these secrets in your essay so others can understand and engage with the world of poetry.
If you still have any questions on how to write a poem analysis essay like a boss, please don’t hesitate to ask our experts for assistance. Whether you need help with a topic, an outline, an initial draft, or proofreading, we are here 24/7 to support your writing endeavors!
Photo by Thought Catalog from Unsplash








